In Blender, cameras are used to capture images. As an important component, this post gives some useful tips about using cameras in Blender animations.
Table of contents
Introduction to camera angles in Blender animations
Apart from a light source and a basic cube, each new Blender scene also opens with a camera object. The camera in Blender is used to capture the rendered image.
This post will show how to use one, or multiple, cameras in a scene, change the size of the camera object and use composite guides.
This post is written to be compatible with Blender versions 2.79b and 2.8. If you find that there are incompatibilities, please let us know in the comments section at the end of this post.
- Get the Wacom Intuos wireless tablet from Amazon.com
- Get the XENCELABS Drawing Tablet from Amazon.com
- Get the LG 22MK430H-B 21.5″ Full HD Monitor from Amazon.com
- Get the ROCCAT Burst Pro PC Gaming Mouse from Amazon.com
Using one camera in Blender
If there is only one camera in the scene, the (then only active) camera view can be toggled at any point by pressing the Numpad 0 key.
The shortcut keys for setting the current view as the active camera view are Ctrl + Alt + Numpad 0 keys while the camera is selected and the mouse pointer is in the 3D view area.
Multiple cameras in Blender
Multiple cameras can also be used in Blender. By adding additional cameras, renders can be made from different camera views in the same scene without having to change one camera each time.
While rendering animations, the render view can be set to jump from one camera to another.
Adding multiple cameras in Blender
More cameras can be added to a scene by pressing the Shift + A keys while in Object Mode and the mouse pointer is in the 3D View area. Additional cameras can be renamed in the Outliner Section to be more descriptive.
Using multiple cameras in Blender
To be able to use a specific camera, it needs to be set to the active camera first. By simply changing the active camera from one to another, different cameras can be used one by one for renders.
To use a specific camera, but only that camera, the active camera can be chosen by selecting it and pressing the Ctrl + Numpad 0 keys. By pressing the Numpad 0 key, that camera’s view will be active.
Using multiple cameras in Blender animation
Additional cameras can be used while rendering animations in Blender. This allows a chosen set of frames to be rendered by one camera, while others can be set to be rendered by using a different camera view.
In Blender, markers can be used to indicate key points or significant events within an animation. It is convenient to indicate (or mark) a change in the active camera while in the viewing and/or rendering process. They also act as stepped keyframes, meaning they will change immediately from the previous frame to the next frame (i.e. there is no interpolation).
One or multiple markers can be used at different locations on the timeline and can be named to give an overview of what change is made.
Before a marker can be used, the camera that needs to be assigned to it needs to be created and named first.
To insert a marker, first, go to the frame it needs to be inserted to and then press the M key while the mouse pointer is in the Timeline View. Alternatively, it can be added by using the Marker menu – Add Marker. This will create a little triangle indicating that that frame has a marker assigned to it.
Markers can be selected and deselected as with everything else in Blender. It will be deselected while hovering over the Timeline View and pressing the A key, and clicking on it with the select mouse button will select it.
By default, markers will be called by the frame number they are situated at. Markers can also be given a descriptive name by pressing Ctrl + M buttons while the mouse pointer is in the Timeline view area.
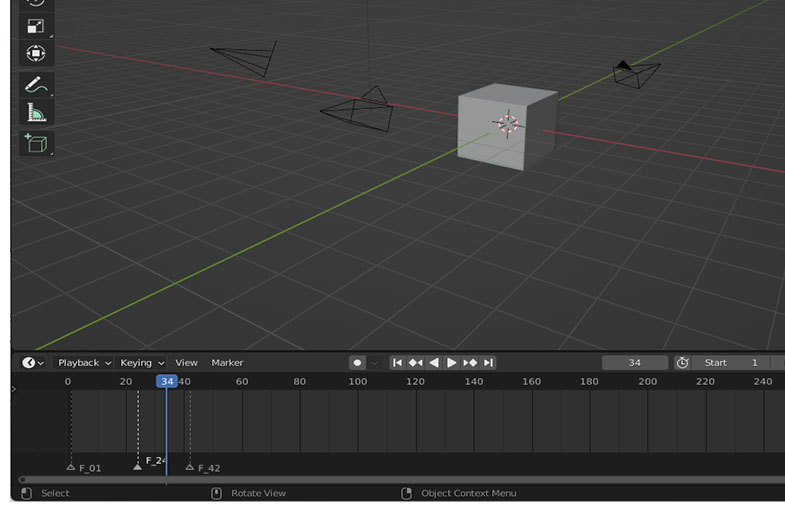
The timeline view area of this scene shows 3 markers (indicated as triangles at frames 1, 24 and 42). The middle marker is active and the first marker has a camera bound to it.
To bind a camera to a marker, it needs to be set to the active camera first. While the camera is active, select the desired marker and hit the Ctrl + B keys while the mouse pointer is in the Timeline View.
Alternatively, the Bind Camera to Markers option under the View menu can be used. The line above the marker triangle will become dotted when a camera is bound.
Change the camera view with the viewport
Instead of working with a camera’s coordinates or moving out of the camera view, in some cases, it might be easier to simply lock the camera to the current active view.
The setting for this is under the Properties panel (visible by either pressing the M button while the mouse pointer is in the 3D view area or by clicking on the + at the top right of the 3D view window).
By checking/unchecking the Lock Camera to View setting, the camera can be moved around while in the Camera view. Remember to uncheck this setting when the camera view has been locked.
Snapping the camera to the centre of the current view
To snap the camera to the centre of the current view, press Ctrl + Alt + Numpad 0 keys on the keyboard. This comes in handy when using the Numpad keys to snap top, left, or right views.
Resetting the camera to its zero position
The default Blender scene camera is positioned above and to the side of the default cube. Its rotation is set to view the default cube from this position.
As with other objects, the camera position and rotation can be reset to their 0 values. By pressing Alt + G, the position of the camera will reset to 0,0,0 and by pressing Alt + R the angle will reset to the Z-axis.
Using common camera resolutions
The Blender camera settings are also used to set the render image resolution. The exact dimension and/or resolution is set under dimensions and resolutions settings situated under the Render tab in the Dimensions section.
Common resolutions can be selected from the Render Presets drop-down list. Custom X and Y values can also be dialled in. The percentage bar below the X and Y values is used as a percentage multiplier to scale the resolutions down. 50% will halve it, and 100% will render at the full resolution. Values for common resolutions:
- 720p – 1280px x 720px
- 1080p – 1920px x 1080px
- 4k – 3840px x 2160px
These are the common and/or recommended resolutions used for the following platforms:
- Facebook – 720p or 1080p for video and 940px x 512px for post images
- Twitter – 720p or 1080p for video and 1200px x 675px for tweet images
- YouTube – 720p, 1080p, 4K
- Pinterest – 1000px x 1000/1500px
- Flickr – 1080p
- WhatsApp – 176px x 144px for video
Using Composition Guides
Blender makes it easy to create better compositions by using their composition guides. Multiple pre-set composite guides are available under the Display settings under the settings of the active camera properties.
Each camera can have its own, single or multiple guides activated. Guidelines will not interfere with rendering.
Changing the camera size
While in Object mode, the camera object outline can be too large or too small to fit the scenes. While in Object mode, the camera outline can be scaled using S. This will not change any of the camera properties.
Conclusion
Useful camera tricks in Blender include adding additional cameras to a scene, resizing the camera object and using composite guides.



