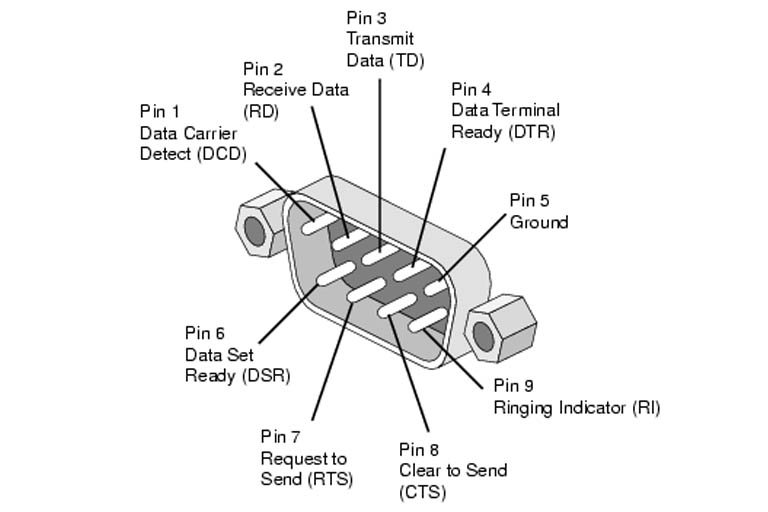
Serial ports are connection ports that transfer data in or out one bit at a time. Data is transferred using two lines, one for transmitting, and one for receiving.
Table of contents
Introduction to serial ports
The serial port is a connection port through which data transfers in or out one bit at a time. Data signals are transferred using two lines, one for transmitting signals (Tx) and one for receiving signals (Rx). Serial ports use the RS-232 standard (also known as recommended standard 232) to determine how data is transmitted.
Serial ports are commonly used for the control, configuration and/or analysis/debugging of RS-232 supported devices. The serial port is a type of device that uses a UART chip (universal asynchronous receiver/transmitter). Data signals are received (Rx) from the communicating device’s transmit (Tx) line and are sent/transmitted (Tx) to the communicating device’s receive (Rx) line.
Serial port connections are used for remote connections to a device. This allows access to a device, using another device containing an interface (third-party interface). Commonly used interfaces include PC-based software and touchscreen devices.
In the audiovisual (AV) field, control processors are also commonly used to be able to connect other devices (i.e. Bluetooth, IR, and Ethernet-connected devices) to integrate control of RS-232 devices.
- Get the FT232RL FTDI USB To TTL Serial Converter Module from Amazon.com or BangGood
- Get the 6 Pin FTDI FT232RL USB To Serial Cable from Amazon.com or BangGood
- Amazon.com or BangGood
The RS-232 standard
Recommended standard 232 defines the electrical characteristics, timing and meaning of data signals and the physical size and pinout of connectors. Other data characteristics include the communication direction (“full duplex” will send and receive data at the same time and “half duplex” will take turns to send and receive data), with or without parity, and/or stop bits.
Serial communication is done by signals representing 1 bit at a time. Each bit is represented by a ‘0’ or a ‘1’. Voltages are used to represent these bits. Bits are determined by ‘inverted logic’ (when compared with TTL/normal logic). By the RS-232 standard, a bit value of ‘1’ is represented by a negative voltage — anywhere from -3 to -25V — while bit value of ‘0’ transmits a positive voltage that can be anywhere from +3 to +25V.
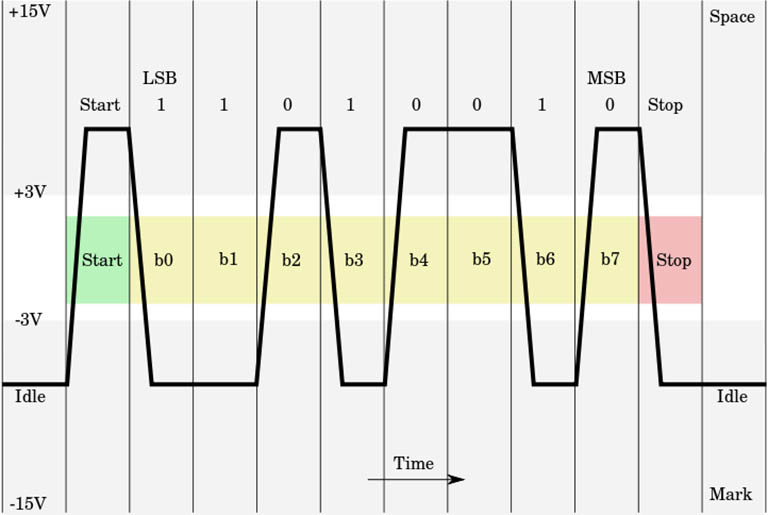
Diagram of RS232 signaling as seen when probed by an Oscilloscope. Image from commons.wikimedia.org.
The more extreme voltages of an RS-232 signal help to make it less susceptible to noise, interference and degradation. This means that an RS-232 signal can generally travel longer physical distances than their TTL counterparts, while still providing a reliable data transmission.
Serial ports on PCs
Some personal computers still have one or two serial ports. In the past, serial ports have been commonly used in PCs to connect to devices such as modems. On most PCs, the data signals swing from -13 to +13V. Zero voltage has no meaning (except it usually means that the unit is powered off). Due to faster and cheaper technology, serial ports have been discontinued by some motherboard manufacturers as standard ports on PCs.
Advantages & disadvantages of the RS-232 interface
Although this technology is fairly old (introduced in 1960), serial ports and the RS-232 interface are easy to use and well-known. The hardware for serial ports is simple to hook up, doesn’t need a lot of wires, is still readily available, and is fairly cheap.
Compared with more modern interfaces, RS 232 is quite slow. There is no clock, meaning the data transmitted/received is asynchronous. Only one device can be connected at a time.
TTL serial connections
Although there are many similarities, RS-232 serial connections are different from TTL (transistor-transistor logic) serial connections. Connecting TTL (3 – 5V) devices directly to a serial port (of, for example, a PC – 13V) may damage the device. PCs can, however, safely use TTL for serial communication by using USB to TTL serial converters.
Conclusion
Serial ports use the RS-232 standard that allows data transfers in or out one bit at a time. Data signals can either be transmitted (Tx) or received (Rx).